- Generate Ethereum Private Key
- Generate Ethereum Private Key Javascript Free
- Generate Ethereum Private Key Javascript Online
- Generate Ethereum Private Key Javascript Download
- Generate Ethereum Private Key Javascript Code
Mining, cryptocurrencies, Ethereum blockchain, crypto trading platforms (here's how to build one, by the way) - this whole relatively new blockchain thing caught my eye a few years ago and the interest only kept increasing.
- Generate Ethereum Wallet from Private Key. Many times users have Private Key and they want to generate Ethereum compatible password protected wallet from that key. Here is a small utility program for Ethereum Blockchain in NodeJS that would help user to generate Ethereum compatible password protected wallet starting just with Private Key.
- So I was starting to try and learn more about cybersecurity and how private keys work, because I find them fascinating. I found a website that generated random private keys, and generated a couple to see what would happen. I know by logic, there is a 1/(2^256) chance of getting a real private key. Well, it happened, and now I don't know what to do.
Consider an Ethereum address as your username and a corresponding private key as the password. While your Ethereum address is public and can be shared, the private key must always be kept secret. Using this combination lets you interact with the Ethereum blockchain. An Ethereum address is your identity on the blockchain, and it looks like this.
I'm saying 'relatively new' because even though the actual concept was devised in 1991, the first practical implementation was effected in 2008 by the elusive Satoshi Nakamoto.
With this brief history behind us, we will focus on the second publicly available blockchain, Ethereum (a more flexible and robust implementation of the concept).
It’s going to be a 4-part series covering the workshops I'm running for my local developers community at FullStack Cluj within the following weeks:
- Build Your Own Private Ethereum Blockchain with Geth
- Build Your Own Private Ethereum Blockchain with Parity
- Setup Proof of Authority Consensus on Private Ethereum Blockchains
- Automate Blockchain Creation with Puppeth.
So let’s get this going.
First off, we need to install Geth which is one of the 3 original implementations (Go, C++ and Pyhton) of the Ethereum protocol.
To install geth on Mac OS X, we assume you already have Homebrew on your machine. In case you don't, follow this link.
Installing geth on Ubuntu is as straightforward as installing any other package.
And for Windows, you can follow this link.
We will now create 2 accounts, one that we'll seed at genesis and another one we'll use for the miner.
To do so, we will run the following command twice and it will ask for a passphrase on each run.
Under no circumstance should you forget the passphrase you're going to set.
This will generate a pair of password-protected public/private keys inside the <data-dir>/keystore folder. By default, Ethereum will store everything inside the <data-dir> folder except for the PoW Ethash DAG.
If datadir parameter is not provided, the default paths for <data-dir> will be used.
- Mac: ~/.ethereum
- Linux: ~/.ethereum
- Windows: %APPDATA%Ethereum
From this point on, consider the following addresses as the ones generated above.
- seed
0x6d5da05a98f04de068418051512f3e965ee8dfca - miner
0x632d167d2eef0f7c1fa37fcc4777d26fe6df944b
The genesis block is what differentiates between all the Ethereum blockchains. Being the first block in the blockchain and having no reference to a previous one, this block is unique in its own way.
Inside the <data-dir> folder we will create a file called genesis.json with the following content:
config
- chainId - this is your chain identifier, it can be any number at random and it will be used in replay protection.
- homesteadBlock, eip155Block, eip158Block, byzantiumBlock - these represent the versions of the blockchain. Since we will start from scratch, all the changes in these versions will be available starting with block 0.
difficulty
This property dictates how hard is to mine a block by directly influencing the nonce applied in the discovery process.
gasLimit
This represents the maximum ammount of gas used on each block. Due to the low mining difficulty we set for the genesis block above, we still want the gas limit pretty high so we don't hit it. This way, we avoid slowing the network.
aloc
In this section we prealocate Ether to the specified accounts. Heads up: this will not create the addresses, you should already have them.
So far, we installed all the prerequisites and configured the node, now the real fun begins.
1. Instantiate The Data Directory
If everything went ok you should have an output similar to this:
2. Start The Node
The networkId we set in the genesis block helps ensuring your network privacy. If other peers want to join your network, they will have to use the same networkId.
The output should be similar to this:
Since we created the accounts with geth inside the same <data-dir> folder and we allocated some Ether in the genesis block to one of the addreses, it was already set as the main account for this instance of the node.
Thus, we can do something like this:
3. Start Another Peer
On the same machine we will start another peer for the miner and for this step we'll create a new <data-dir> (let's call it <peer-data-dir>), copy the miner private key generated above inside the keystore folder, and then start a new peer.
We will then initialize the data dir.
Then start the second peer.
The output should be similar to the one we had above, the difference being the default address which should be the miner one.
4. Connect Peers Together
To connect the peers together we require the enode address of the first peer. To get this, in the console of the initial peer we run:
This should return something like:
With this information we run in the console of the second peer:
5. Start The Miner
Checking the initial balance of the miner account should return 0 as we did not prealocate any funds to this account.
Next, we set the miner address as the payout address for the miner.
And then we start the miner.
After generating the DAG, the miner should start pushing blocks.
And the initial peer should start importing.
Once we stop the miner and check the balance again, we see that after 20 blocks mined the account has 60 Ether.
Having gotten this far, you should now have a basic understanding of how to set up you private Ethereum blockchain.
As mentioned in the introduction, you're currently reading the first article in a series so if you want to build your blockchain further, make sure you check the next one (by following Around25 on Twitter, LinkedIn, or Facebook). There, we’ll dig in a different implementation of the Ethereum protocol by parity.
Oh, and one more thing: want to challenge the ideas above, ask any questions or just learn more about how we do blockchain? Check this page or request our expertise here.
Overview
- NodeJS installed on your system.
- A text editor
- Terminal aka Command Line
What is an Ethereum address?
- Receiving/Sending Ethereum currency
- Signing/Sending transactions
- Connecting to decentralized applications
How an Ethereum address is generated:
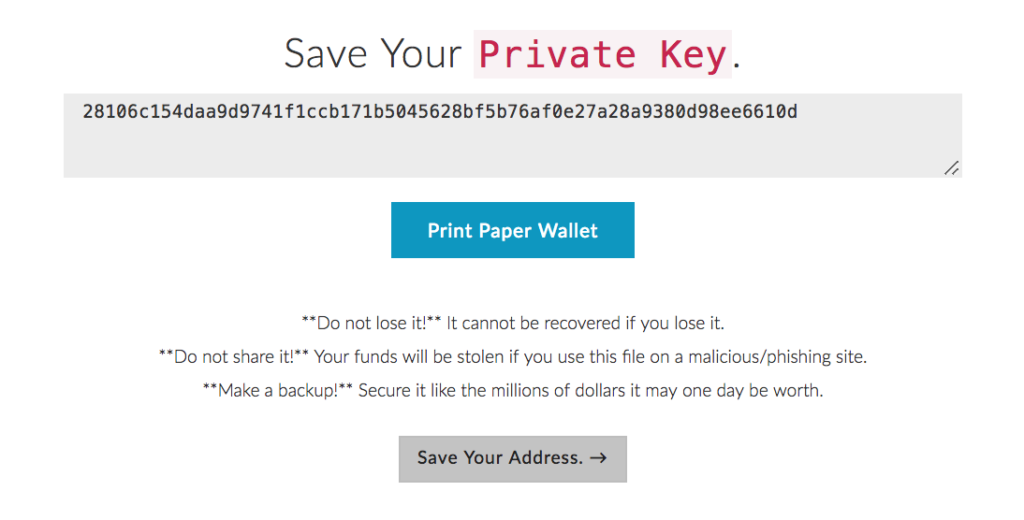
- A random private key of 64 (hex) characters (256 bits / 32 bytes) is generated first.
For example:
- A 128 (hex) character (64 bytes) public key is then derived from the generated private key using Elliptic Curve Digital Signature Algorithm (ECDSA).
For example:
- The Keccak-256 hash function is then applied to (128 characters / 64 bytes) the public key to obtain a 64 character (32 bytes) hash string. The last 40 characters / 20 bytes of this string prefixed with 0x become the final Ethereum address.
For example:
Note: 0x in coding indicates that the number/string is written in hex.
Generate Ethereum Private Key
What is ethers.js?
Generating an Ethereum address in JavaScript


Note: You will need to have your python version match one of the compatible versions listed in the instructions above if you encounter the node-gyp issue.
Generate Ethereum Private Key Javascript Free
Generate Ethereum Private Key Javascript Online
Conclusion
- Overview
- What is an Ethereum address?
- How an Ethereum address is generated:
- What is ethers.js?
- Generating an Ethereum address in JavaScript
- Conclusion
Share article
Want more Web3 tuts?
We'll send you the latest tech and tutorials via our weekly Web3 Vibes newsletter.
Related articles 16
Mar 20, 2021 How to connect to Ethereum using .NET (Nethereum)Dotnet or .NET is very popular for the development of desktop applications, most Windows desktop applications are built using .NET, and it also contributes largely to web application’s tech stack. In this guide, let’s see how we can connect to Ethereum using .NET and
Generate Ethereum Private Key Javascript Download
Continue reading Mar 20, 2021 How to fetch Ethereum event logs in Ruby
How to fetch Ethereum event logs in RubyEthereum log records are very useful to understand and keep track of smart contract events. In this guide, we are going to learn how to fetch ethereum event logs in Ruby using ethereum.rb ruby...
Continue reading Mar 20, 2021 How to generate a new Ethereum address in GoGolang is very popular among backend developers for building infrastructures and microservices. Go is a procedural programming language. Developed in 2007 by Robert Griesemer, Rob Pike, and Ken Thompson at Google, then launched in 2009 as...
Continue reading Mar 20, 2021 How to generate a new Ethereum address in PythonPython is one of the most versatile programming languages out there with an abundance of use cases; We can build many applications with Python from client-side to back end. In this guide, we will cover creating an Ethereum address in Python using the
Continue reading Mar 20, 2021 How to connect to the Ethereum network using Ruby
How to connect to the Ethereum network using RubyRuby has a huge fanbase. Ruby was developed by its creator with an intention to create a language people can have fun using. Ruby has been largely accepted by the developers all around the world since it’s launch, in fact, the biggest tech communities in many cities are...
Continue reading Mar 20, 2021 How to connect to the Ethereum network using Python using Web3.pyYou can build Ethereum applications in different programming languages. In this article, we will connect to the Ethereum network using Python.PrerequisiteEthereum Node (We will use QuikNode’s free...
Continue reading Mar 20, 2021 How to connect to Ethereum network with ethers.jsWhen someone thinks of developing a dApp the first tool that comes to their mind is web3.js which is pretty common because of its popularity in the community and wide use cases, dApp development has been consistently growing and there are a lot of developers who want to...
Continue reading Mar 20, 2021 How to re-send a transaction with higher gas price using ethers.jsSometimes, you submit a transaction on Ethereum without enough gas due to network congestion or too many pending transactions offering a higher gas price than you have offered on your transaction. If you have a high priority transaction but low gas, you could end up...
Continue reading Mar 20, 2021 How to connect to Ethereum network with Web3.jsLibraries and frameworks make the development process a lot easier and faster. When it comes to Ethereum development, Web3.js is the go to library. That's because Web3.js is the official library, from the
Continue reading Mar 20, 2021 How to use Subspace with QuikNodeIn this guide, we'll understand a bit about reactive development and how to use Subspace with QuikNode.JavaScript is the programming language behind most of the internet apps and websites. JavaScript today has become one of the most used programming languages, and...
Continue reading Mar 20, 2021 How to generate a new Ethereum address in RubyWith high usage in web applications and straightforward syntax, Ruby is used by a vast number of people. This guide will cover creating an Ethereum address in Ruby using ruby-eth...
Generate Ethereum Private Key Javascript Code
Continue reading Mar 20, 2021 How to connect to Ethereum network using Java / Web3jWe can say that Java is one of the most versatile languages out there, and it continues to be relevant in today's time. Java is so popular because of its massive user base and use cases. In this guide/tutorial, we'll learn how to connect to the Ethereum Blockchain network...
Continue reading Mar 31, 2021 How to generate a new Ethereum address in PHPPHP is very popular in developing the backend of websites or web applications. PHP has a huge crowd of developers trusting it as their go-to language. In this guide, we will see how we can generate a new Ethereum address in...
Continue reading Apr 13, 2021 How to Fork Ethereum Blockchain with Ganache.Forking and running a local simulated Ethereum environment is essential if you want to work with DeFi or do Ethereum development in general. In this guide, we’ll cover how to fork Ethereum Blockchain with
Continue reading Mar 20, 2021 Estimating gas price using pending transactions in PythonTo send a transaction on the Ethereum network, you need to pay fees for including the transaction in a block as well as the computation necessary in the transaction; this fee is called gas. The transactions are accepted into the block based on the amount of gas they are...
Continue reading Mar 20, 2021 How to connect to Ethereum network using GoGo helps you make faster scalable backends and this guide will show you how to connect your backend to Ethereum (and make it even faster, more reliable, and globally accessible, all thanks to QuikNode’s global infrastructure). What is...
Continue reading