- Intune App Wrapping Tool Download
- Intune App Wrapping Tool Online
- Intune App Wrapping Tool Windows 10
- Intune App Wrapping Tool Mac
- One of the most frequently asked questions from customers is whether it is possible to publish Win32 applications with Microsoft Intune. The answer is Yes. It is possible to deploy Windows 10 Store Apps, MSI files and even.EXE files. Although.EXE files cannot be published directly. You need to “wrap” the.EXE file (and other required source files if applicable) to an.INTUNEWIN file.
- May 28, 2015 Microsoft recently released the Microsoft Intune App Wrapping Tool for Android that allows you to take your Line of Business (LOB) apps and make them managed. By making an app managed, you add an extra layer of restrictions around the app to restrict operations like cut, copy and paste or open web links in a managed browser.
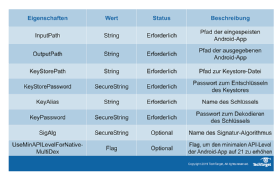
Mar 25, 2021 Windows application size is capped at 8 GB per app. Convert the Win32 app content. Use the Microsoft Win32 Content Prep Tool to pre-process Windows classic (Win32) apps. The tool converts application installation files into the.intunewin format. The tool also detects some of the attributes that Intune requires to determine the application.
Use the information in this article to help you add macOS line-of-business apps to Microsoft Intune. You must download an external tool to pre-process your .pkg files before you can upload your line-of-business file to Microsoft Intune. The pre-processing of your .pkg files must take place on a macOS device.
Note
Starting with the release of macOS Catalina 10.15, prior to adding your apps to Intune, check to make sure your macOS LOB apps are notarized. If the developers of your LOB apps did not notarize their apps, the apps will fail to run on your users' macOS devices. For more information about how to check if an app is notarized, visit Notarize your macOS apps to prepare for macOS Catalina.
macOS LOB apps have a maximum size limit of 2 GB per app.
While users of macOS devices can remove some of the built-in macOS apps like Stocks, and Maps, you cannot use Intune to redeploy those apps. If end users delete these apps, they must go to the app store, and manually re install them.
Before your start
You must download an external tool, mark the downloaded tool as an executable, and pre-process your .pkg files with the tool before you can upload your line-of-business file to Microsoft Intune. The pre-processing of your .pkg files must take place on a macOS device. Use the Intune App Wrapping Tool for Mac to enable Mac apps to be managed by Microsoft Intune.
Important
The .pkg file must be signed using 'Developer ID Installer' certificate, obtained from an Apple Developer account. Only .pkg files may be used to upload macOS LOB apps to Microsoft Intune. However, conversion of other formats, such as .dmg to .pkg is supported. For more information about converting non-pkg application types, see How to deploy DMG or APP-format apps to Intune-managed Macs.
Download the Intune App Wrapping Tool for Mac.
Note
The Intune App Wrapping Tool for Mac must be run on a macOS machine.
Mark the downloaded tool as an executable:
- Start the terminal app.
- Change the directory to the location where
IntuneAppUtilis located. - Run the following command to make the tool executable:
chmod +x IntuneAppUtil
Use the
IntuneAppUtilcommand within the Intune App Wrapping Tool for Mac to wrap .pkg LOB app file from a .intunemac file.Sample commands to use for the Microsoft Intune App Wrapping Tool for macOS:
Important
Ensure that the argument
<source_file>does not contain spaces before running theIntuneAppUtilcommands.IntuneAppUtil -h
This command will show usage information for the tool.IntuneAppUtil -c <source_file> -o <output_directory_path> [-v]
This command will wrap the .pkg LOB app file provided in<source_file>to a .intunemac file of the same name and place it in the folder pointed to by<output_directory_path>.IntuneAppUtil -r <filename.intunemac> [-v]
This command will extract the detected parameters and version for the created .intunemac file.
Select the app type
- Sign in to the Microsoft Endpoint Manager admin center.
- Select Apps > All apps > Add.
- In the Select app type pane, under the Other app types, select Line-of-business app.
- Click Select. The Add app steps are displayed.
Step 1 - App information
Select the app package file
- In the Add app pane, click Select app package file.
- In the App package file pane, select the browse button. Then, select an macOS installation file with the extension .intunemac.The app details will be displayed.
- When you're finished, select OK on the App package file pane to add the app.
Set app information
- In the App information page, add the details for your app. Depending on the app that you chose, some of the values in this pane might be automatically filled in.
- Name: Enter the name of the app as it appears in the company portal. Make sure all app names that you use are unique. If the same app name exists twice, only one of the apps appears in the company portal.
- Description: Enter the description of the app. The description appears in the company portal.
- Publisher: Enter the name of the publisher of the app.
- Minimum Operating System: From the list, choose the minimum operating system version on which the app can be installed. If you assign the app to a device with an earlier operating system, it will not be installed.
- Ignore app version: Select Yes to install the app if the app is not already installed on the device. Select No to only install the app when it is not already installed on the device, or if the deploying app's version number does not match the version that's already installed on the device.
- Install as managed: Select Yes to install the Mac LOB app as a managed app on supported devices (macOS 11 and higher). A macOS LOB app can only be installed as managed when the app distributable contains a single app without any nested packages and installs to the /Applications directory. Managed line-of-business apps will be able to be removed using the uninstall assignment type on supported devices (macOS 11 and higher). In addition, removing the MDM profile removes all managed apps from the device. The default value is No.
- Category: Select one or more of the built-in app categories, or select a category that you created. Categories make it easier for users to find the app when they browse through the company portal.
- Show this as a featured app in the Company Portal: Display the app prominently on the main page of the company portal when users browse for apps.
- Information URL: Optionally, enter the URL of a website that contains information about this app. The URL appears in the company portal.
- Privacy URL: Optionally, enter the URL of a website that contains privacy information for this app. The URL appears in the company portal.
- Developer: Optionally, enter the name of the app developer.
- Owner: Optionally, enter a name for the owner of this app. An example is HR department.
- Notes: Enter any notes that you want to associate with this app.
- Logo: Upload an icon that is associated with the app. This icon is displayed with the app when users browse through the company portal.
- Click Next to display the Scope tags page.
Step 2 - Select scope tags (optional)
You can use scope tags to determine who can see client app information in Intune. For full details about scope tags, see Use role-based access control and scope tags for distributed IT.
- Click Select scope tags to optionally add scope tags for the app.
- Click Next to display the Assignments page.
Step 3 - Assignments
- Select the Required, Available for enrolled devices, or Uninstall group assignments for the app. For more information, see Add groups to organize users and devices and Assign apps to groups with Microsoft Intune.
- Click Next to display the Review + create page.
Step 4 - Review + create
Review the values and settings you entered for the app.
When you are done, click Create to add the app to Intune.
The Overview blade for the line-of-business app is displayed.
The app you have created appears in the apps list where you can assign it to the groups you choose. For help, see How to assign apps to groups.
Note
If the .pkg file contains multiple apps or app installers, then Microsoft Intune will only report that the app is successfully installed when all installed apps are detected on the device.
Update a line-of-business app
- Sign in to the Microsoft Endpoint Manager admin center.
- Select Apps > All apps.
- Find and select your app from the list of apps.
- Select Properties under Manage from the app pane.
- Select Edit next to App information.
- Click on the listed file next to Select file to update. The App package file pane is displayed.
- Select the folder icon and browse to the location of your updated app file. Select Open. The app information is updated with the package information.
- Verify that App version reflects the updated app package.
Note
For the Intune service to successfully deploy a new .pkg file to the device you must increment the package version and CFBundleVersion string in the packageinfo file in your .pkg package.
Next steps
The app you have created is displayed in the apps list. You can now assign it to the groups you choose. For help, see How to assign apps to groups.
Learn more about the ways in which you can monitor the properties and assignment of your app. For more information, see How to monitor app information and assignments.
Learn more about the context of your app in Intune. For more information, see Overview of device and app lifecycles
In the first blog about the Microsoft Intune App-layer protection, one of the supported features is that you are able to wrap your own applications with the Microsoft Intune App Wrapping Tool for iOS so that you are able to manage those applications with the Mobile Application Management policies. In this second blog in the series, we will have a look at the Microsoft Intune App Wrapping Tool for iOS.
With this blog I want to show two scenarios. One with an application with no policies active and one with the same application that is wrapped with the Microsoft Intune App Wrapping Tool with the mobile application policies active. To be able to do this I have created a very basic application with two “pages” and on each page, there is a text field where I can type text and copy and paste it within the application and beyond.
Meet Notepad 🙂
Page 2 of Notepad |
Again it is a very basic and uggly app, but it does its work 🙂 (Okay I will try to make it more fancy 😉 )
Intune App Wrapping Tool Download
That being said, when looking at the Microsoft Intune App Wrapping Tool for iOS, you need to be sure that the following prerequisites are in place:
- You need to have an Apple Developer Account
- You need to have access to a Mac OS X 10.8.5 or later with xcode
- You need to have a Provisioning Profile
- You need to have a distribution certificate
- Your device needs to be based on iOS 7.01 or later
- A developed iOS LOB Application.
Unmanaged Application
So when deploying the standard application via Microsoft Intune, you are able to install it and copy and paste the “Super secret text” between the pages in the Notepad application and for instance the email application within the iOS device.
Create a managed application
Intune App Wrapping Tool Online
So the default created application can be deployed without any problem. What we need to do next is to wrap the Notepad application with the Microsoft Intune App Wrapping Tool to allow management via Microsoft Intune.
You can download the Microsoft Intune App Wrapping Tool for iOS supporting the right language here. Next you need to extract the DMG file to a folder where you are able to access the IntuneMAMPackager tool, TechNet describes to start the command line tool like this ./IntuneMAMPackager.app/Contents/MacOS/IntuneMAMPackager but I also extracted the content from the file to be able to access the IntuneMAMPackager file directly.
The IntuneMAMPackager tool has the following parameters that you may need to add to be able to wrap your application.
| Parameter | Description |
| -i | The path and file name of the source application. (mandatory) |
| -o | The path in which to save the wrapped application. (mandatory) |
| -p | The path of your provisioning profile for iOS applications. (mandatory) |
| -c | The SHA1 hash of the signing certificate (Optional). |
| -a | The Client ID of the input app (in GUID format) if the app uses Azure Active Directory Libraries (Optional). |
| -t | The path to a test mobile application management policy file for testing outside of Intune (Optional). |
| -r | Redirect URI of the input app if the app uses Azure Active Directory Libraries (Optional). |
| -v | Verbose messages while wrapping the application. |
For my Notepad application I need to start the following command line at the console of the Mac OS X device;
./IntuneMAMPackager –i ./Notepad-v1.ipa –p XC_Ad_Hoc_.mobileprovisioning –o ./Notepad- wrapped.ipa –c 679cd10b63499c3f89c6edfb07d2e2b80dfb0d
Application wrapped by the Microsoft Intune App Wrapping Tool
That you cannot wrap every IPA file is true since the wrapping tool cannot wrap the following apps;
- Encrypted apps
- Unsigned apps
- Apps with extended file attributes
Trying to wrap an app that is not signed by Apple
In the next blog we will add the application to Microsoft Intune, deploy it and have a look how the Mobile Application Management Policies can be applied to the managed application.
Intune App Wrapping Tool Windows 10
Till next time.